(with Agarwal, Morais and Shue), 2024
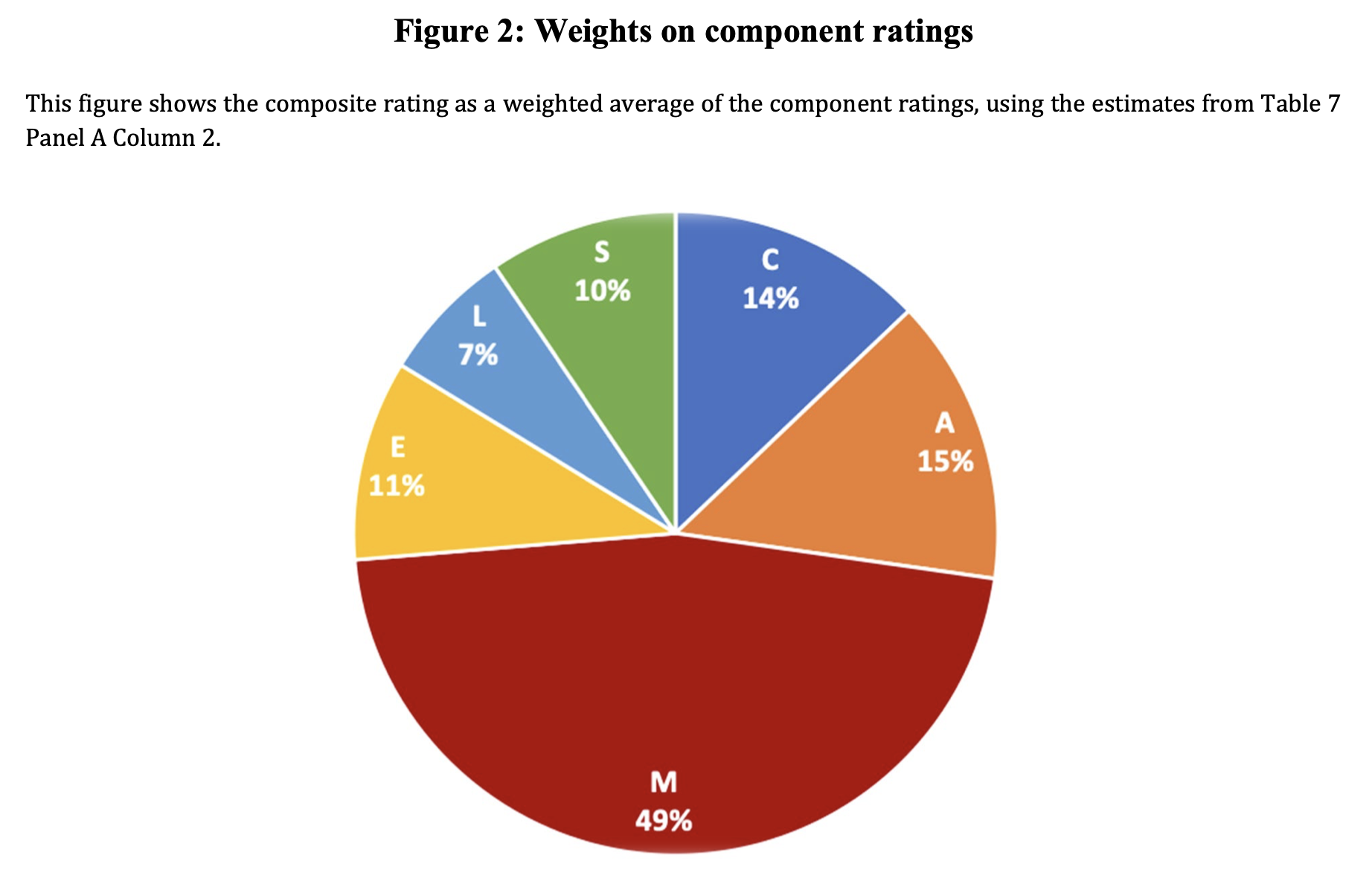
While reliance on human discretion is a pervasive feature of institutional design, human discretion can also introduce costly noise (Kahneman, Sibony, and Sunstein 2021). We evaluate the consequences, determinants, and trade-offs associated with discretion in high-stake decisions assessing bank safety and soundness. Using detailed data on the supervisory ratings of US banks, we find that professional bank examiners exercise significant personal discretion—their decisions deviate substantially from algorithmic benchmarks and can be predicted by examiner identities, holding bank fundamentals constant. Examiner discretion has a large and persistent causal impact on future bank capitalization and supply of credit, leading to volatility and uncertainty in bank outcomes, and a conservative anticipatory response by banks. We identify a novel source of noise: weights assigned to specific issues. Disagreement in ratings across examiners can be attributed to high average weight (50%) assigned to subjective assessment of banks’ management quality, as well as heterogeneity in weights attached to more objective issues such as capital adequacy. Replacing human discretion with a simple algorithm leads to worse predictions of bank health, while moderate limits on discretion can translate to more informative and less noisy predictions.
(with Buchak, Matvos and Piskorski), 2024
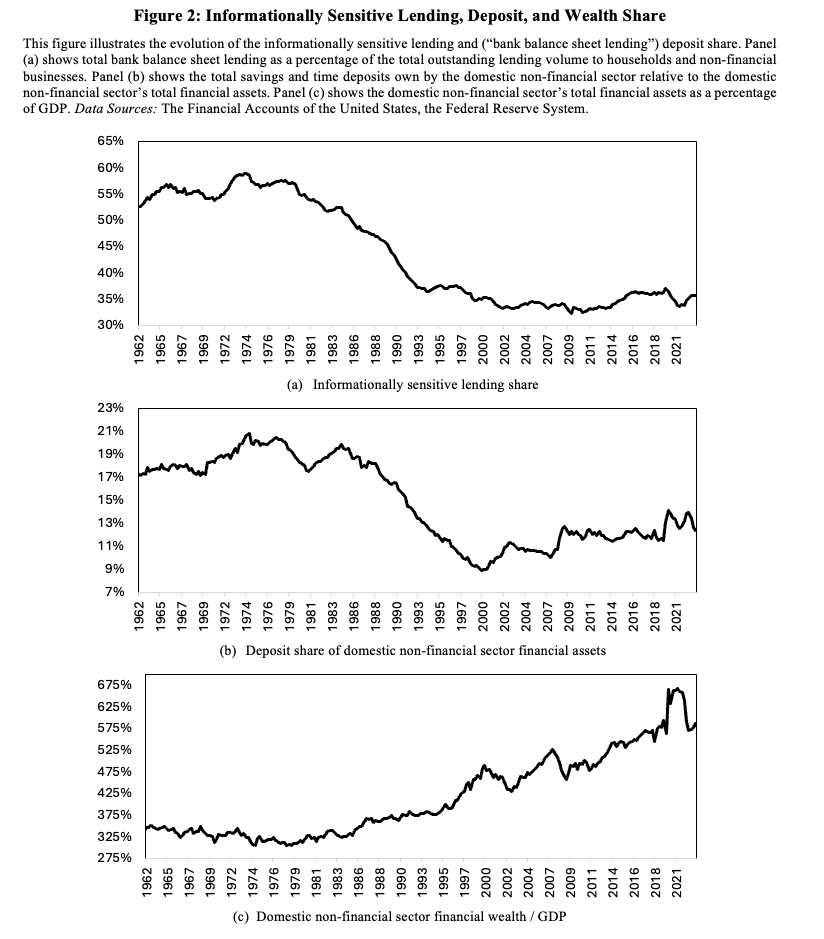
The traditional model of bank-led financial intermediation, where banks issue demandable deposits to savers and make informationally sensitive loans to borrowers, has seen a dramatic decline since 1970s. Instead, private credit is increasingly intermediated through arms-length transactions, such as securitization. This paper documents these trends, explores their causes, and discusses their implications for the financial system and regulation. We document that the balance sheet share of overall private lending has declined from 60% in 1970 to 35% in 2023, while the deposit share of savings has declined from 22% to 13%. Additionally, the share of loans as a percentage of bank assets has fallen from 70% to 55%. We develop a structural model to explore whether technological improvements in securitization, shifts in saver preferences away from deposits, and changes in implicit subsidies and costs of bank activities can explain these shifts. Declines in securitization cost account for changes in aggregate lending quantities. Savers, rather than borrowers, are the main drivers of bank balance sheet size. Implicit banks’ costs and subsidies explain shifting bank balance sheet composition. Together, these forces explain the fall in the overall share of informationally sensitive bank lending in credit intermediation. We conclude by examining how these shifts impact the financial sector’s sensitivity to macroprudential regulation. While raising capital requirements or liquidity requirements decreases lending in both early (1960s) and recent (2020’s) scenarios, the effect is less pronounced in the later period due to the reduced role of bank balance sheets in credit intermediation. The substitution of bank balance sheet loans with debt securities in response to these policies explains why we observe only a fairly modest decline in aggregate lending despite a large contraction of bank balance sheet lending. Overall, we find that the intermediation sector has undergone significant transformation, with implications for macroprudential policy and financial regulation.
(with Jiang, Matvos and Piskorski), 2024
In the face of rising interest rates in 2022, banks mitigated interest rate exposure of the accounting value of their assets but left the vast majority of their long-duration assets exposed to interest rate risk. Data from call reports and SEC filings shows that only 6% of U.S. banking assets used derivatives to hedge their interest rate risk, and even heavy users of derivatives left most assets unhedged. The banks most vulnerable to asset declines and solvency runs decreased existing hedges, focusing on short-term gains but risking further losses if rates rose. Instead of hedging the market value risk of bank asset declines, banks used accounting reclassification to diminish the impact of interest rate increases on book capital. Banks reclassified $1 trillion in securities as held-to-maturity (HTM) which insulated these assets book values from interest rate fluctuations. More vulnerable banks were more likely to reclassify. Extending Jiang et al.’s (2023) solvency bank run model, we show that capital regulation could address run risk by encouraging capital raising, but its effectiveness depends on the regulatory capital definitions and can by eroded by the use of HTM accounting. Including deposit franchise value in regulatory capital calculations without considering run risk could weaken capital regulation’s ability to prevent runs. Our findings have implications for regulatory capital accounting and risk management practices in the banking sector.
(with Jiang, Matvos and Piskorski), 2024
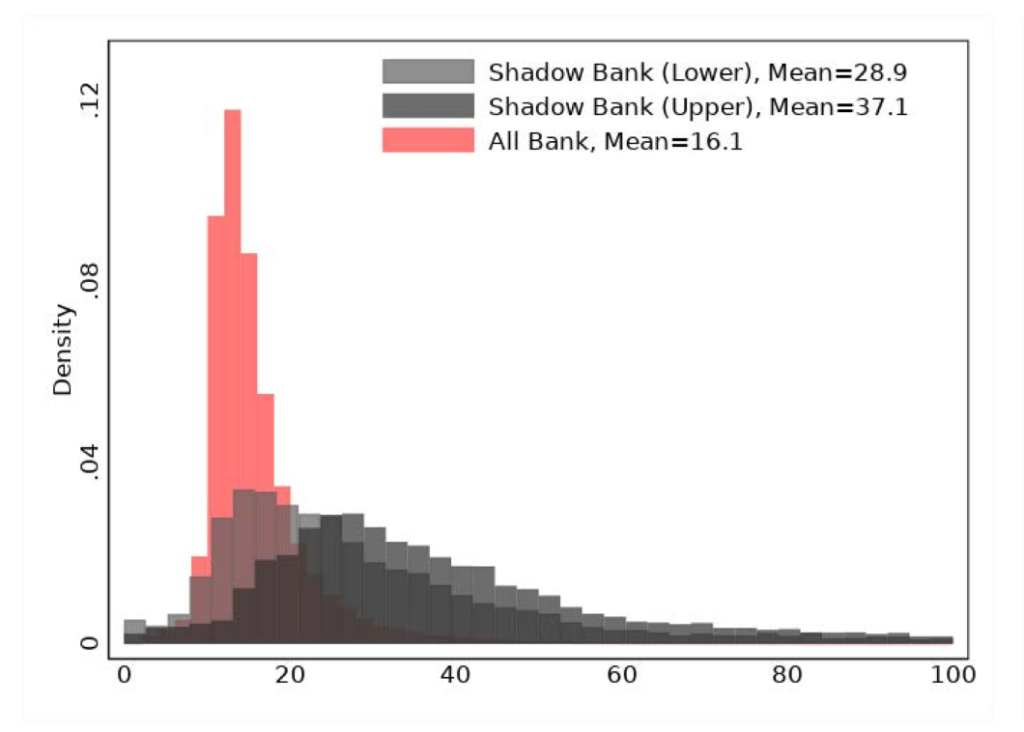
We examine why banks maintain such high financial leverage, with debt financing accounting for about 90% of banks’ assets. To answer this question, we use uniquely assembled data on capital structure decisions of shadow banks that on the asset side conduct very similar business to banks. The shadow bank data provides us with a window into “free market” financing choices of financial intermediaries that unlike banks are lightly regulated and do not have access to insured deposit funding. We demonstrate that shadow banks employ twice the amount of equity capital compared to equivalent banks, with the most significant disparity observed between smaller and mid-size banks. Uninsured leverage, defined as uninsured debt funding to assets, increases with size for both banks and shadow banks while cost of debt declines with size. We rationalize these facts within a calibrated quantitative equilibrium model of intermediation. Our analysis reveals that the primary driver of high leverage among smaller and mid-size banks is their access to insured deposit funding. In the absence of deposit insurance, these banks would maintain a capitalization level at least 25% higher in relative terms than observed in the data. Conversely, deposit insurance plays a comparatively minor role in influencing the financial leverage of the largest banks, where the predominant factor is their capacity to generate money-like deposits. These results suggest a significant scope for the increase of capitalization of smaller and mid-size banks to align their capital structures with their private market counterparts. The aggregate consequences of such increase would be limited, because of reallocation of lending activity from smaller to large banks and to shadow banks.
(with Jiang, Matvos and Piskorski), 2023
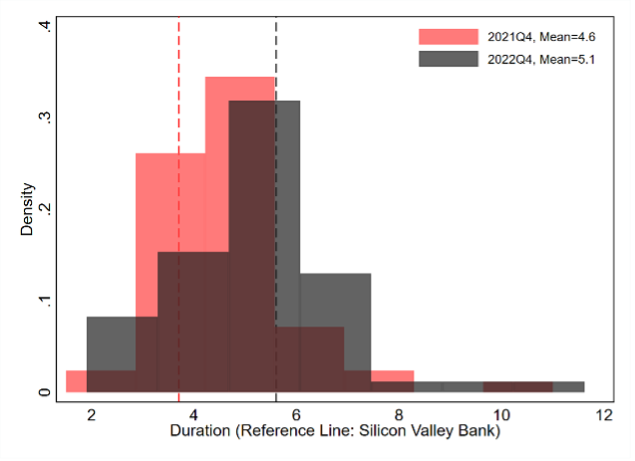
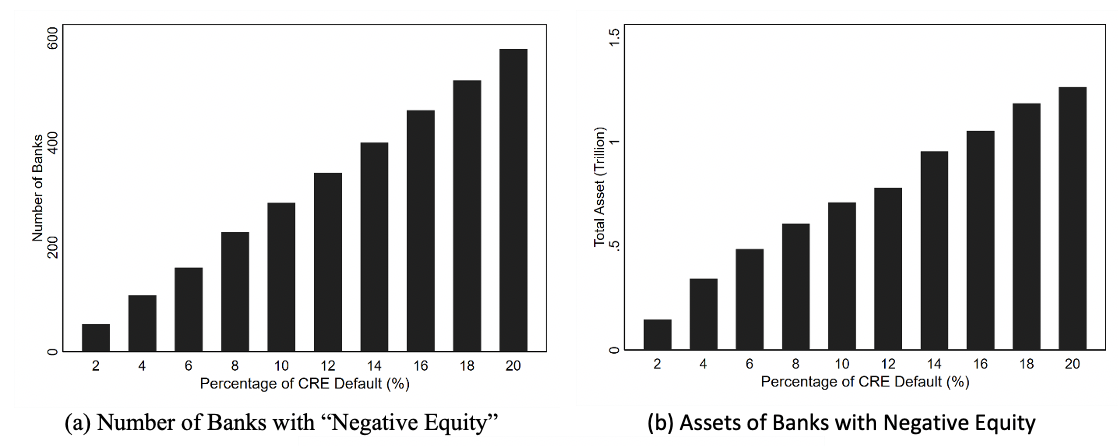
We develop an empirical methodology and conceptual framework to analyze the effect of rising interest rates on the value of U.S. bank assets and bank stability. We mark-to-market losses on banks’ assets due to interest rate increases from Q1 2022 to Q1 2023. Asset values declined on average by 10%, and the $2.2 trillion aggregate decline was on the order of aggregate bank capital. We present a model of solvency runs, which illustrates that interest rate increases can lead to self-fulfilling solvency bank runs even when banks’ assets are fully liquid. The model identifies banks with asset losses, low capital, and critically, high uninsured leverage as being most fragile. A case study of the recently failed Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) confirms the model insights. 10 percent of banks have larger unrecognized losses and lower capital than SVB. On the other hand, SVB had a disproportional share of uninsured funding: only 1 percent of banks had higher uninsured leverage. Combined, losses and uninsured leverage provided incentives for an SVB uninsured depositor run. We compute new empirical measures of bank fragility for the sample of all U.S. banks. Even if only half of uninsured depositors had decided to withdraw, almost 190 banks with assets of $300 billion are at a potential risk of insolvency, meaning that the mark-to-market value of their remaining assets after these withdrawals would be insufficient to repay all insured deposits. We briefly discuss events and subsequent research following our paper’s release on March 13, 2023. We see these as providing validity to our approach and findings.
with Buchak, Matvos and Piskorski), 2023 (R&R, Journal of Political Economy)
We study the frictions in dealer-intermediation in residential real estate through the lens of “iBuyers,” technology entrants, who purchase and sell residential real estate through online platforms. iBuyers supply liquidity to households by allowing them to avoid a lengthy sale process. They sell houses quickly and earn a 5% spread. Their prices are well explained by a simple hedonic model, consistent with their use of algorithmic pricing. iBuyers choose to intermediate in markets that are liquid, and in which automated valuation models have low pricing error. These facts suggest that iBuyers’ speedy offers may come at the cost of information loss concerning house attributes that are difficult to capture in an algorithm, resulting in adverse selection. We calibrate a dynamic structural search model with adverse selection to understand and quantify the economic forces underlying the tradeoffs of dealer intermediation in this market. The model reveals the central tradeoff to intermediating in residential real estate. To provide valuable liquidity service, transactions must be closed quickly. Yet, the intermediary must also be able to price houses accurately to avoid adverse selection, which is difficult to accomplish quickly. We find that low underlying liquidity exacerbates adverse selection. Our analysis suggests that iBuyers’ technology provides a middle ground: they can transact quickly limiting information loss. Even with this technology, intermediation is only profitable in the most liquid and easy to value houses. Therefore, iBuyers’ technology allows them to supply liquidity, but only in pockets where it is relatively least valuable. We also find limited scope for dealer intermediation even with improved pricing technology, suggesting that underlying liquidity will be an impediment for intermediation in the future.
(with Artavanis, Paravisini, Robles-Garcia and Tsoutsoura), 2023
We develop a new approach to identify different categories of depositors during periods of uncertainty and quantify their compensation to remain in the bank. We isolate withdrawals due to liquidity needs, deterioration of fundamentals, and expectation about withdrawal behavior of other depositors. We exploit variation in the cost of withdrawal induced by the maturity expiration of time deposits around unexpected uncertainty events and high-frequency microdata from a large Greek bank. Deposit withdrawals quadrupled in response to a policy uncertainty shock that doubled the short-run credit default swap (CDS) price of Greek sovereign bonds. About two-thirds of this increase is driven by direct exposure to deteriorating fundamentals, and the remainder due to strategic complementarities. We find that depositors need to be offered annualized returns exceeding 50% to remain in the bank during episodes of high uncertainty. Our findings provide new insights into the design of interventions that prevent runs by targeting depositors with the largest propensity to withdraw.
From Rotten Apples to Rotten Orchards: Labor Market Sorting and Wrongdoing in the Financial Advisor Industry
(with Vicinanza, Egan, Rao and Matvos, 2023
(with Liberti and Vig), 2017. (R&R Journal of Financial Economics)
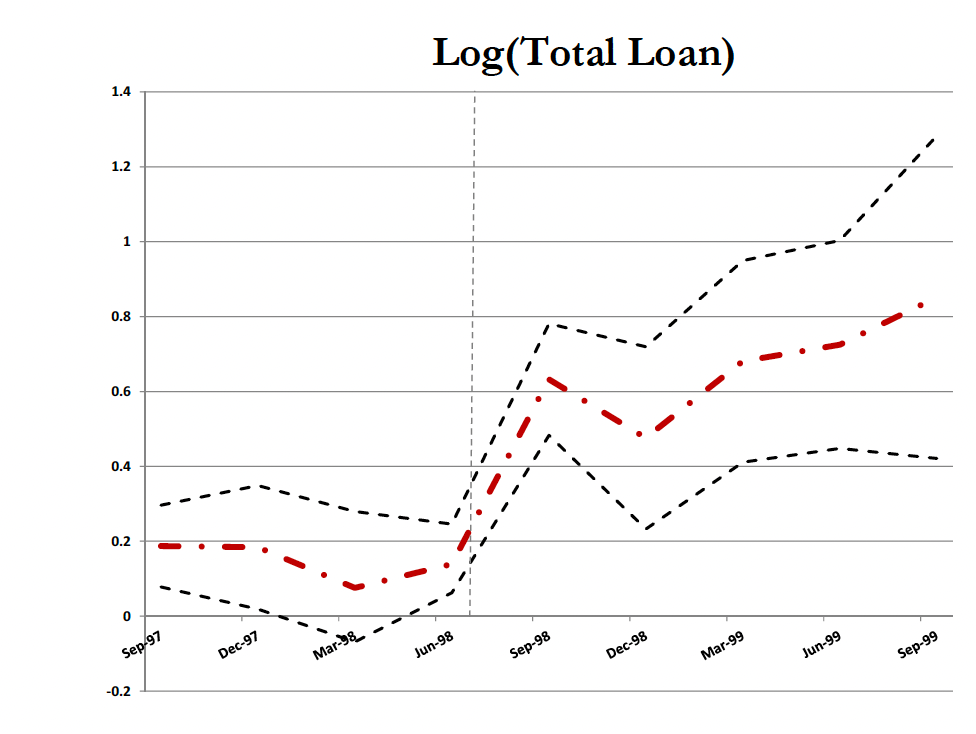
This paper investigates the effect of a change in informational environment of borrowers on the organizational design of bank lending. We use micro-data from a large multinational bank and exploit the sudden introduction of a credit registry, an information-sharing mechanism across banks, for a subset of borrowers. Using within borrower and loan officer variation in a difference-in-difference empirical design, we show that expansion of credit registry led to an improvement in allocation of credit to affected borrowers. There was a concurrent change in the organizational structure of the bank that involved a dramatic increase in delegation of lending decisions of affected borrowers to loan officers. We also find a significant expansion in scope of activities of loan officers who deal primarily with affected borrowers, as well as of their superiors. There is suggestive evidence that larger banks in the economy were better able to implement similar changes as our bank. We argue that these patterns can be understood within the framework of incentive-based and information cost processing theories. Our findings could help rationalize why improvements in the information environment of borrowers may be altering the landscape of lending by moving decisions outside the boundaries of financial intermediaries.
(with Agarwal, Benmelech and Bergman), 2012. (R&R Journal of Political Economy)
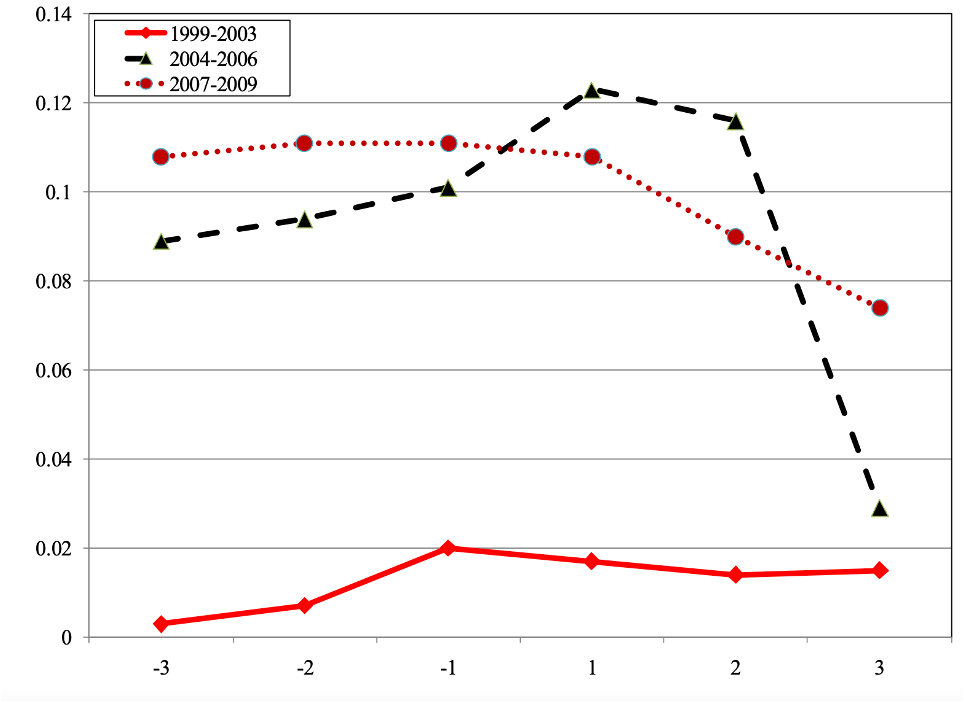
Yes, it did. We use exogenous variation in banks’ incentives to conform to the standards of the Community Reinvestment Act (CRA) around regulatory exam dates to trace out the effect of the CRA on lending activity. Our empirical strategy compares lending behavior of banks undergoing CRA exams within a given census tract in a given month to the behavior of banks operating in the same census tract-month that do not face these exams. We find that adherence to the act led to riskier lending by banks: in the six quarters surrounding the CRA exams lending is elevated on average by about 5 percent every quarter and loans in these quarters default by about 15 percent more often. These patterns are accentuated in CRA-eligible census tracts and are concentrated among large banks. The effects are strongest during the time period when the market for private securitization was booming.